Difference between revisions of "Projects Overview"
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
The [[WRF Hindcast]] project generates the input data used by the [[Grow Degree Calculator]] (GDC) and the [[Soil Moisture Estimator]] (SME) applications. WRF stands for Weather, Research, and Forecasting and is a program made available by [http://www.wrf-model.org/index.php UCAR/NCAR] and other research participants. We use WRF to calculate a virtual weather station at a 3.3km resolution on an hourly basis for about half of the Western United States. | The [[WRF Hindcast]] project generates the input data used by the [[Grow Degree Calculator]] (GDC) and the [[Soil Moisture Estimator]] (SME) applications. WRF stands for Weather, Research, and Forecasting and is a program made available by [http://www.wrf-model.org/index.php UCAR/NCAR] and other research participants. We use WRF to calculate a virtual weather station at a 3.3km resolution on an hourly basis for about half of the Western United States. | ||
| − | This project is fully operational and is the backbone of the GDC and SME applications. | + | This project is fully operational, and is the backbone of the GDC and SME applications. |
== Grow Degree Calculator == | == Grow Degree Calculator == | ||
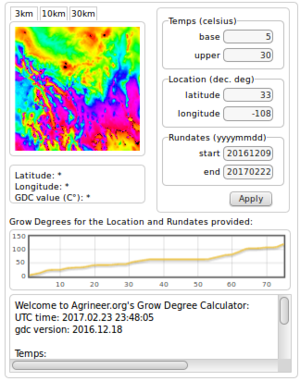
| − | The [[Grow Degree Calculator]] project is based on the | + | [[File:GDC.png|300px|thumb|right|Grow Degree Calculator application.]] |
| + | The [[Grow Degree Calculator]] project is based on the WRF Hindcast project and calculates the Grow Degree values for both crops and insects. Users can enter a location, a start and end date with lower and upper temps for the organism of interest. Output includes a text report, a plot of accumulated values over time, and an image the total accumulated values over the target sector. Click [http://agrineer.org/gdc/gdc.php here] to use the GDC application. | ||
| − | This project is fully operational. | + | This project is fully operational, but requires studies to determining accuracy. |
== Soil Moisture Estimator == | == Soil Moisture Estimator == | ||
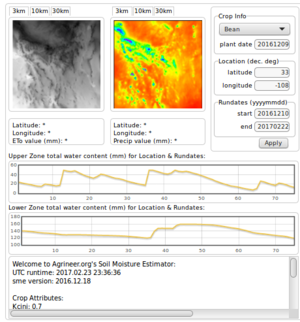
| + | [[File:SME.png|300px|thumb|right|Soil Moisture Estimator application.]] | ||
| + | The [[Soil Moisture Estimator]] project is also based on the WRF Hindcast project and estimates the soil moisture at a given location. A more sophisticated program than the GDC, this application requires crop and soil information provided by the user. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The standard reference evapotranspiration, ETo, is calculated on an hourly basis for a daily total. The ETo calculation is based on the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) method given in this [http://www.fao.org/docrep/X0490E/x0490e04.htm paper]. The calculated ETo values and the WRF precipitation values give the atmospheric loads at the soil surface. The loads are presented to our implementation of the [http://www.nws.noaa.gov/oh/hrl/nwsrfs/users_manual/part2/_pdf/23sacsma.pdf Sacramento Soil Moisture Accounting] model for soil moisture estimation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This project is fully operational, but requires studies to determining accuracy. | ||
| + | |||
== Soil Moisture Radar == | == Soil Moisture Radar == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Soil Moisture Radar project implements a Software Defined Radio (SDR) bi-static radar, using GPS signals, to estimate soil moisture. GPS signals are ubiquitous and suited for top layer soil penetration. The difference between a signal that has reflected | ||
| + | through the soil and one that has not gives an indicator of soil moisture. The signals to compare are derived from one antenna point up (direct and normal usage) with an antenna pointing down. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This project is under development and is conducted jointly with our sister laboratory, PlanetaryImaging.org | ||
Revision as of 18:53, 5 March 2017
Brief description of current and future projects are presented below.
WRF Hindcast
The WRF Hindcast project generates the input data used by the Grow Degree Calculator (GDC) and the Soil Moisture Estimator (SME) applications. WRF stands for Weather, Research, and Forecasting and is a program made available by UCAR/NCAR and other research participants. We use WRF to calculate a virtual weather station at a 3.3km resolution on an hourly basis for about half of the Western United States.
This project is fully operational, and is the backbone of the GDC and SME applications.
Grow Degree Calculator
The Grow Degree Calculator project is based on the WRF Hindcast project and calculates the Grow Degree values for both crops and insects. Users can enter a location, a start and end date with lower and upper temps for the organism of interest. Output includes a text report, a plot of accumulated values over time, and an image the total accumulated values over the target sector. Click here to use the GDC application.
This project is fully operational, but requires studies to determining accuracy.
Soil Moisture Estimator
The Soil Moisture Estimator project is also based on the WRF Hindcast project and estimates the soil moisture at a given location. A more sophisticated program than the GDC, this application requires crop and soil information provided by the user.
The standard reference evapotranspiration, ETo, is calculated on an hourly basis for a daily total. The ETo calculation is based on the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) method given in this paper. The calculated ETo values and the WRF precipitation values give the atmospheric loads at the soil surface. The loads are presented to our implementation of the Sacramento Soil Moisture Accounting model for soil moisture estimation.
This project is fully operational, but requires studies to determining accuracy.
Soil Moisture Radar
The Soil Moisture Radar project implements a Software Defined Radio (SDR) bi-static radar, using GPS signals, to estimate soil moisture. GPS signals are ubiquitous and suited for top layer soil penetration. The difference between a signal that has reflected through the soil and one that has not gives an indicator of soil moisture. The signals to compare are derived from one antenna point up (direct and normal usage) with an antenna pointing down.
This project is under development and is conducted jointly with our sister laboratory, PlanetaryImaging.org